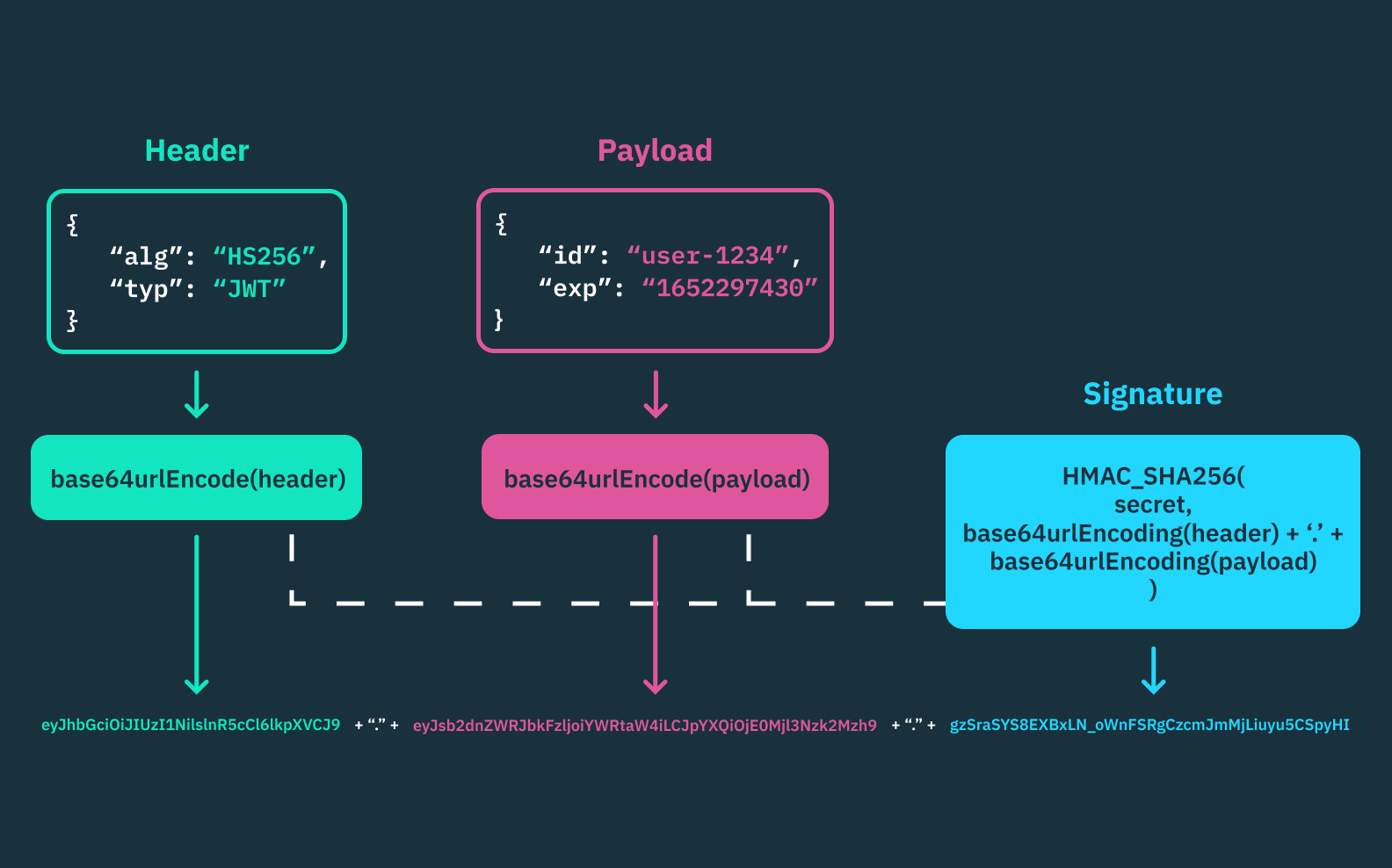
JSON Web Tokens (JWT)¶
Header¶
Payload¶
Common claim types:
iss(Issuer): Identifies who issued the token.sub(Subject): Represents the user or entity the token is about.aud(Audience): Specifies the intended recipient.exp(Expiration): Defines when the token expires.iat(Issued At): Timestamp when the token was created.nbf(Not Before): Specifies when the token becomes valid.
Signature¶
The signature is created by taking the encoded header, the encoded payload, a secret key, and the algorithm specified in the header. The signature ensures that the token hasn't been altered.